We consider motion of the stars in the Galaxy with a model axially symmetrical potential which becomes quasi-spherical at large distances from the galactic center and gives rise to the observed galactic rotation curve. As an example we have taken the galactic potential as in Paczynsky (1990) paper. The potential consists of two disk components corresponding to the galactic disc and the buldge
![]()
and of a quasi-spherical halo with density distribution in the form
![]()
The parameters of the potential are the following:
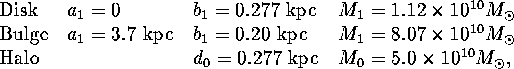
here ![]()