Next: The Environment of the Up: ``Ecology'' of Magnetic Rotators Previous: ``Ecology'' of Magnetic Rotators
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: The
Environment of the Up: ``Ecology''
of Magnetic Rotators Previous: ``Ecology''
of Magnetic Rotators
In this review, we shall call any gravitationally-bounded object having
an angular momentum and intrinsic magnetic field by
the term ``gravimagnetic rotator'' or simply, rotator.
In order to specify the intrinsic properties of the rotator, three parameters
are sufficient - the mass M, the total angular momentum ![]() (I is the moment of inertia and
(I is the moment of inertia and ![]() is the angular velocity), and the magnetic dipole moment
is the angular velocity), and the magnetic dipole moment ![]() (see Figure 3). Given the rotator radius
(see Figure 3). Given the rotator radius
![]() , one can express the magnetic field strength at the
poles
, one can express the magnetic field strength at the
poles ![]() by using the dipole moment
by using the dipole moment ![]() . The angle
. The angle ![]() between the angular moment
between the angular moment ![]() and the magnetic dipole moment
and the magnetic dipole moment ![]() can also be of importance:
can also be of importance: ![]() .
.
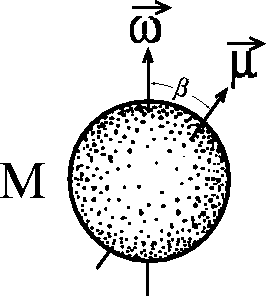
Figure 3: Schematic representation of a gravimagnetic rotator.